Solar water pumps can supply water to locations which are beyond the reach of power lines. Commonly, such places rely on human or animal power or on diesel engines for their water supply or where the frequent power cuts are observed and the power when available is not pure and enough (Indian Conditions in Rural). Solar water pumps can replace the current pump systems and result in both socioeconomic benefits as well as climate related benefits as well as the existing pump can also be driven using highly efficient Control Electronics with MPPT which maximize the Solar Power extraction. The water supplied by the solar water pump can be used to irrigate crops, water livestock or provide potable drinking , cooking and sanitation water.
A solar water pump system is essentially an electrical pump system in which the electricity is provided by one or several Photo Voltaic (PV) panels. A typical solar powered pumping system consists of a solar panel array that powers an electric motor, which in turn powers a bore or surface pump. The water is often pumped from the ground or stream into a storage tank that provides a gravity feed, so energy storage is not needed for these systems
There are two main types of solar water pump technologies:
a) The centrifugal pump, which uses high speed rotation to suck water in through the middle of the pump. Most conventional Alternating Current (AC) pumps use such a centrifugal impeller. However, when operating at low power the performance of the pump drops dramatically. This makes centrifugal pumps less suitable for solar applications, since low power due to cloudy weather is to be expected; and
b) The positive displacement pump, which usually uses a piston to transfer water. Many solar water pumps use the positive displacement pump, which brings water into a chamber and then forces it out using a piston or helical screw. These types generally pump slower than other types of pumps, but have good performance under low power conditions and can achieve high lift. Since PV is expensive and is an intermittent power supplier, solar pumps need to be as efficient as possible. Efficiency of the pump is measured in the amount of water pumped per watt of electricity used.
Two types of pump exist
a) Submersible pumps and b) surface pumps.
It depends on the water source which pump type is more suitable. In the case of a well, the pump needs to be placed underwater. Surface pumps can be placed at the side of a lake or, in the case of a floating pump, on top of the water. Surface pumps are less expensive than submersible pumps, but they are not well suited for suction and can only draw water from about 6.5 vertical meters. Surface pumps are excellent for pushing water over long distances.
All types of Water Pumps are available as per your requirement

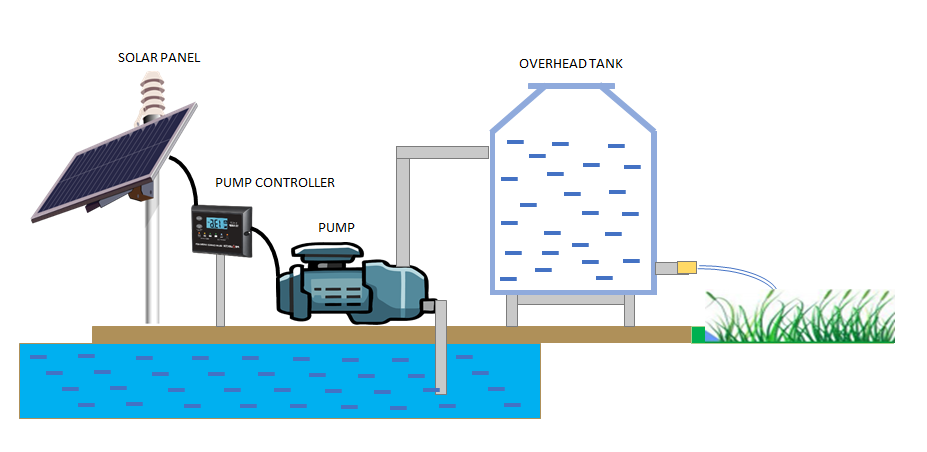
How do Solar Well Pumps Work?
-
Solar panels create power (direct current) when the sun is shining.
-
That power runs through the connected wires to the Pump Controller (the gray box pictured).
-
Optimized voltage is transmitted down the well to the submersible well pump.
-
The well pump then pushes water up through the connected plumbing (usually PVC or black poly pipe) to a hose bib or into a holding tank. If the high-water tank sensor or the low-water well sensor connected to the Pump Controller is activated, the pump will stop running to prevent overflowing the tank or running the pump dry.
-
Water can be used directly with a gravity-fed system or can be pressurized/boosted.
For additional gallons per day and as a 24/7 backup, 12V deep-cycle batteries can be added to power the pump. The Pump Controller also acts as a solar charge controller to keep your batteries safely topped off!
